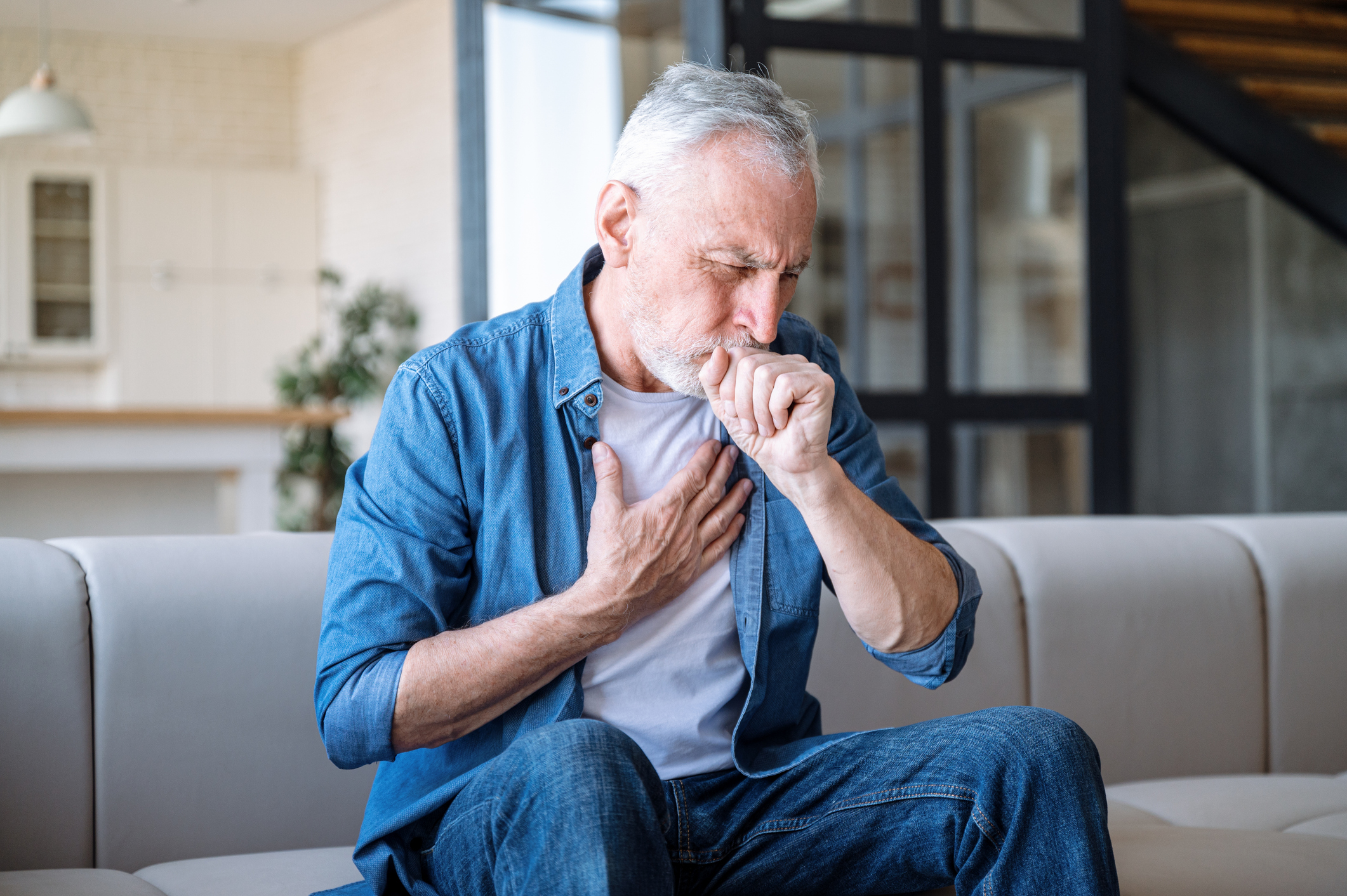
A new study presented atthe American Thoracic Society 2025 International Conference indicates that rilzabrutinib treatment is associated with fewer loss of asthma control (LOAC) events in patients with poorly controlled moderate to severe asthma. Study participants taking the medication used short-acting β2 adrenergic agonist (SABA) rescue medication less often over 12 weeks than participants receiving placebo.
“Achieving meaningful improvements in asthma control remains an unmet need,” wrote the authors, led by William W. Busse, MD, of the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison.
Rilzabrutinib is an investigational, oral, reversible, covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. In a previous phase 2 proof-of-concept study, the drug was associated with fewer LOAC events. The current study was a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with two staggered cohorts of adults with moderate to severe asthma who were poorly controlled on inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and/or long-acting β2 adrenergic agonist (LABA) therapy.
The researchers assessed the use of rescue medications in 196 eligible patients who were randomized first to rilzabrutinib 800 mg (400 mg twice a day; n=32) or placebo (n=32), then to rilzabrutinib 1,200 mg (400 mg three times a day; n = 64) or placebo (n = 68). The study drug was first added to medium- to high-dose ICS/LABA, which was then withdrawn during weeks 4 through 9.
The researchers defined a LOAC event as use of six or more SABA puffs in 24 hours for two consecutive days. Patients receiving 800 mg rilzabrutinib reported that level of SABA use at a rate of 6.3% versus 12.5% with placebo (relative risk reduction [RRR]=50%). Those receiving 1,200 mg rilzabrutinib had 0% LOAC events versus 10.3% in those receiving placebo (RRR=100%).
Reference
Busse WW, Maspero JF, Pavord ID, et al. Reduction in the use of rescue medication for asthma symptom relief with rilzabrutinib: results from a phase 2 study. Abstract #A1298. Presented at the American Thoracic Society International Conference; May 18-21, 2025; San Francisco, California.